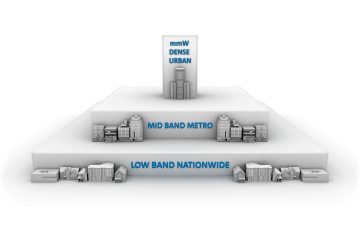
Mobile devices are all around us – in homes, office buildings, hotels, hospitals, factories, airports, and more – and new digital applications are emerging all the time. Increasingly, these applications require the higher speeds made possible by 5G networks.
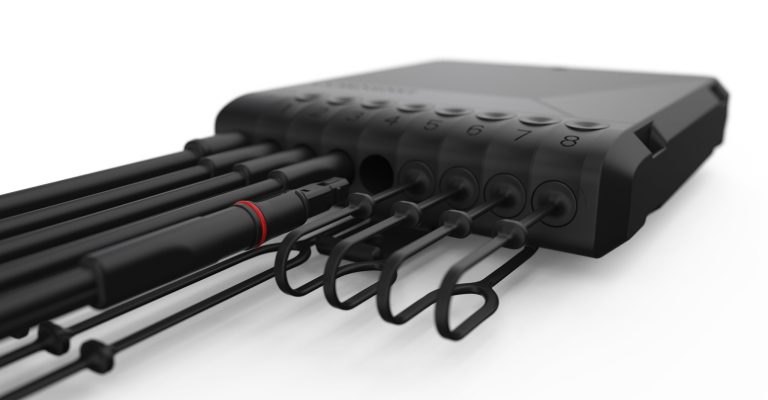
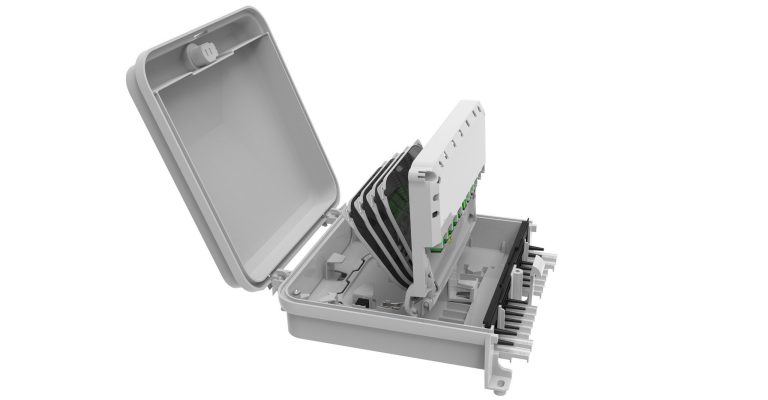
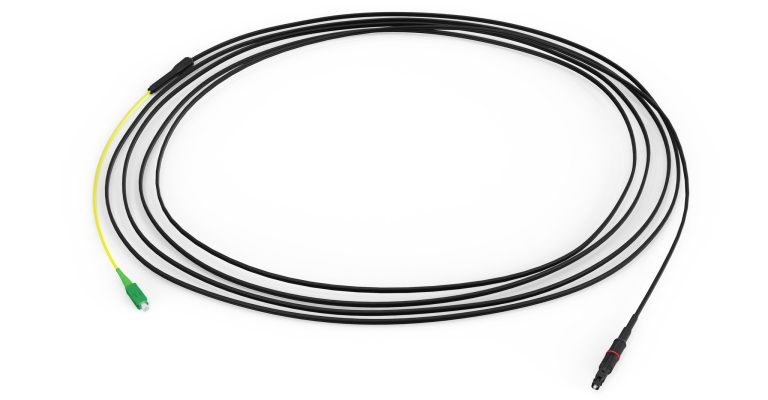
These networks are only wireless “at the edge,” that is, from the antennas to our mobile phones. Behind those antennas is a wired infrastructure that uses large amounts of optical fiber, hair-thin specialized glass developed by Corning scientists to accommodate the extreme increase of data rates driven by the new applications.