Project Mercury
NASA’s Project Mercury sent the first Americans into space. Corning’s heat-resistant windows for the Mercury protected the spacecraft and its passengers from the dangerously high temperatures involved with launch and atmospheric re-entry. This began Corning’s long-standing relationship with NASA.
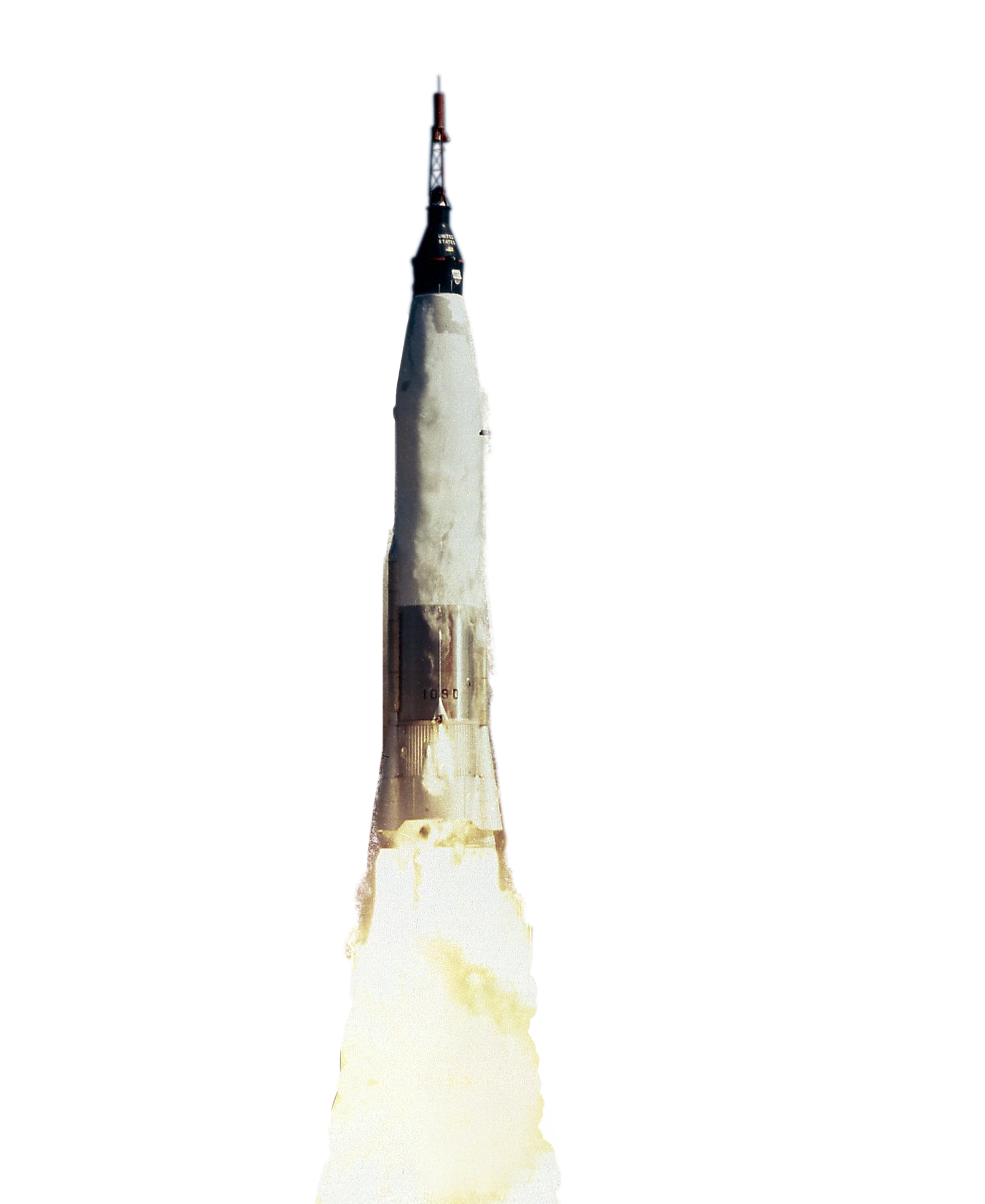

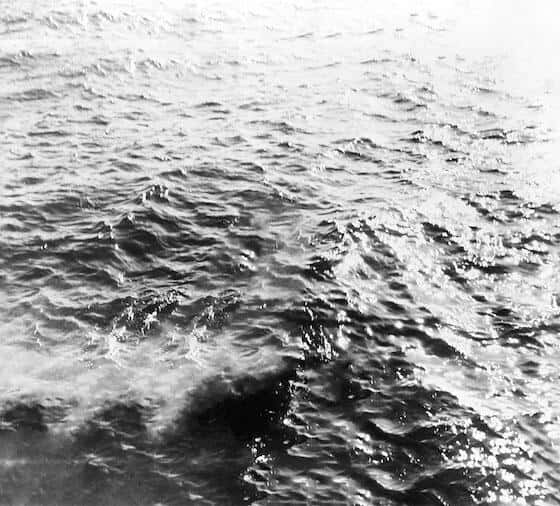
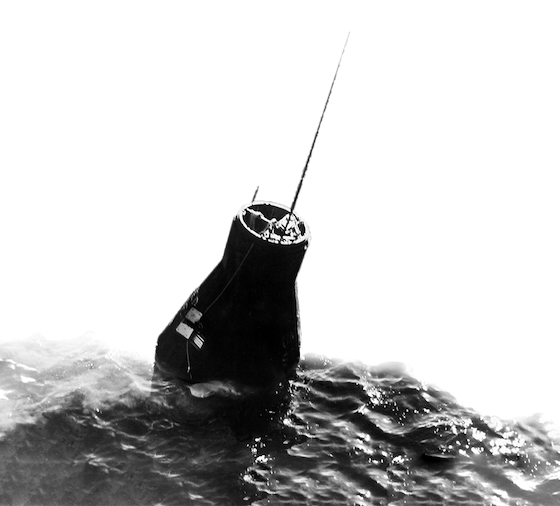
Friendship 7
The Friendship 7 featured Corning window glass for astronaut and senator John Glenn’s historic orbit of the Earth mission.
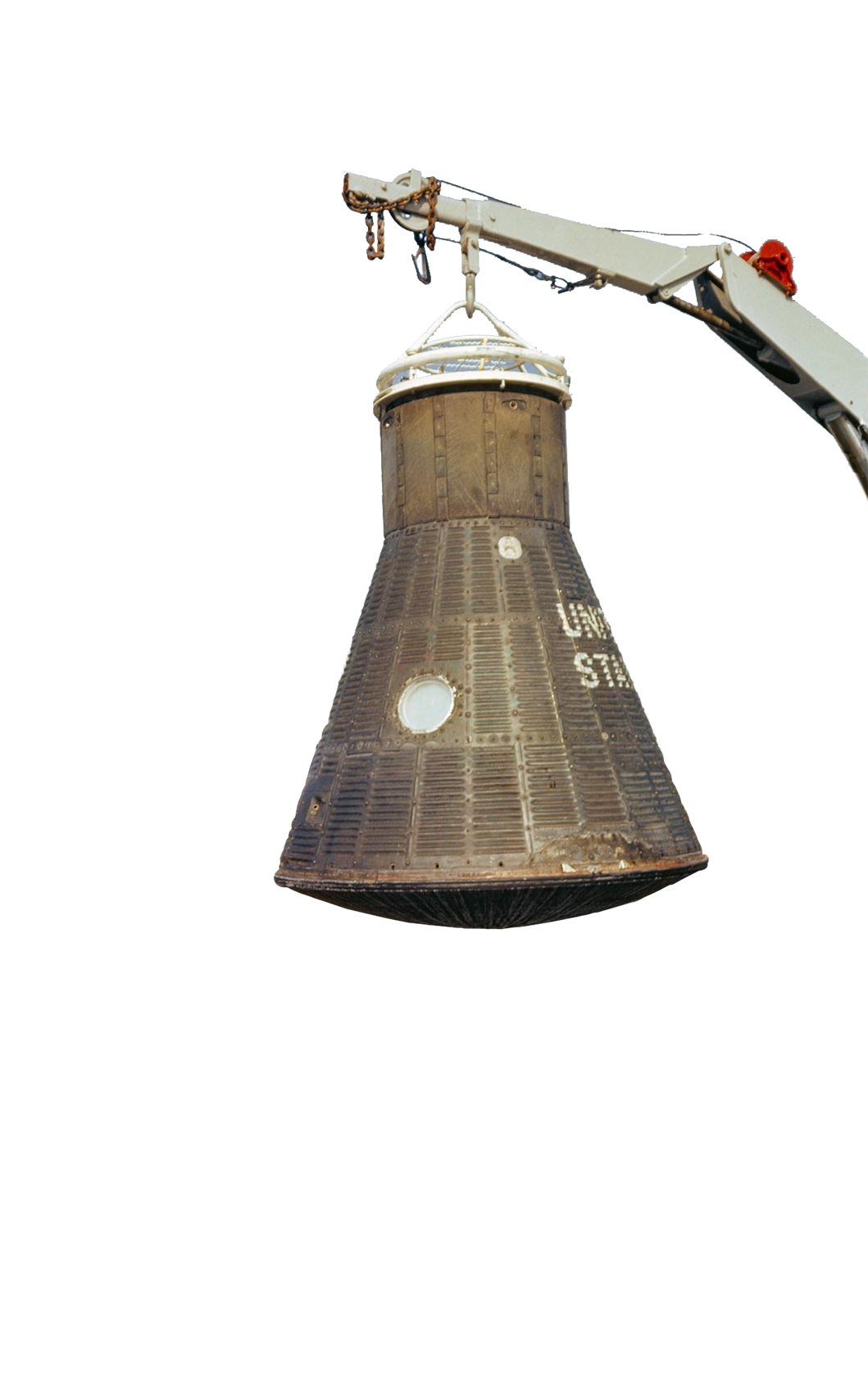




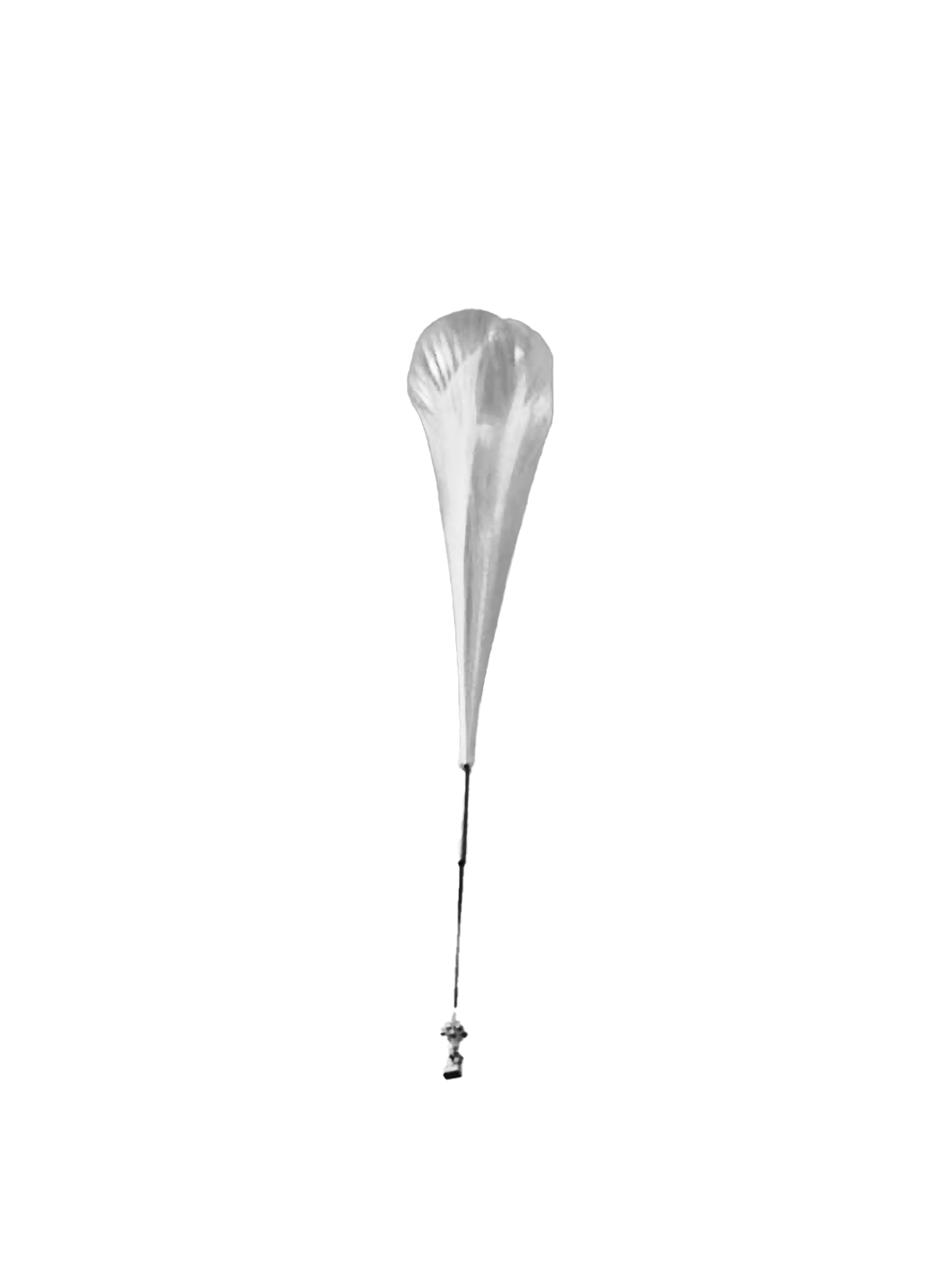
Stratoscope II Telescope
Corning® HPFS® Fused Silica was used for the first large telescope mirror blank in the 36-inch Stratoscope II, a telescope flown by balloons and controlled from the ground.


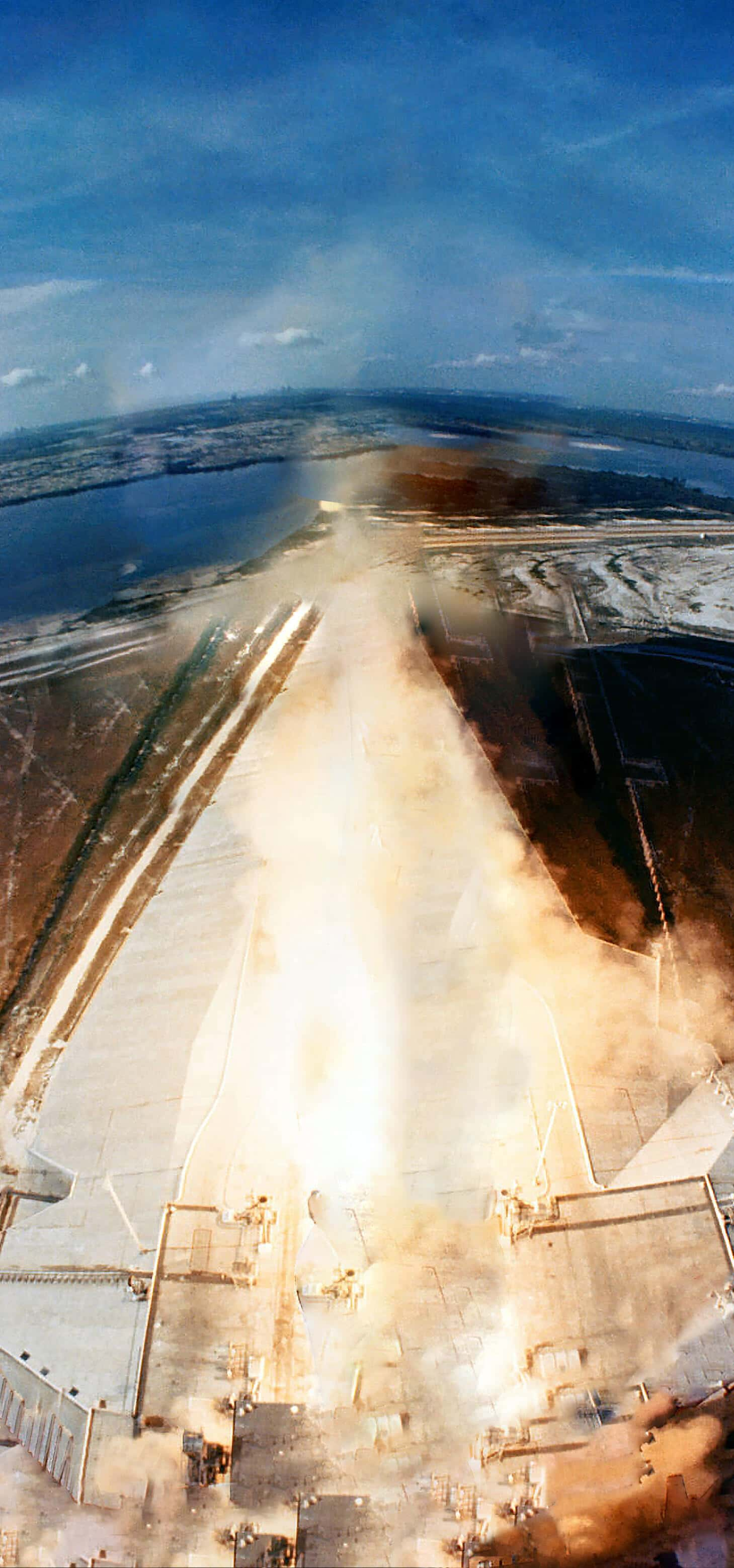
Apollo 11
Corning’s fused silica was used in the Apollo 11 Lunar Module for the heat-shield windows. The Apollo 11 was the first crewed vehicle to land on the moon.


Space Shuttle
In the early 1970s, Corning began manufacturing fused silica space shuttle windows for NASA. Corning has supplied every window for every American-manned space shuttle to date.
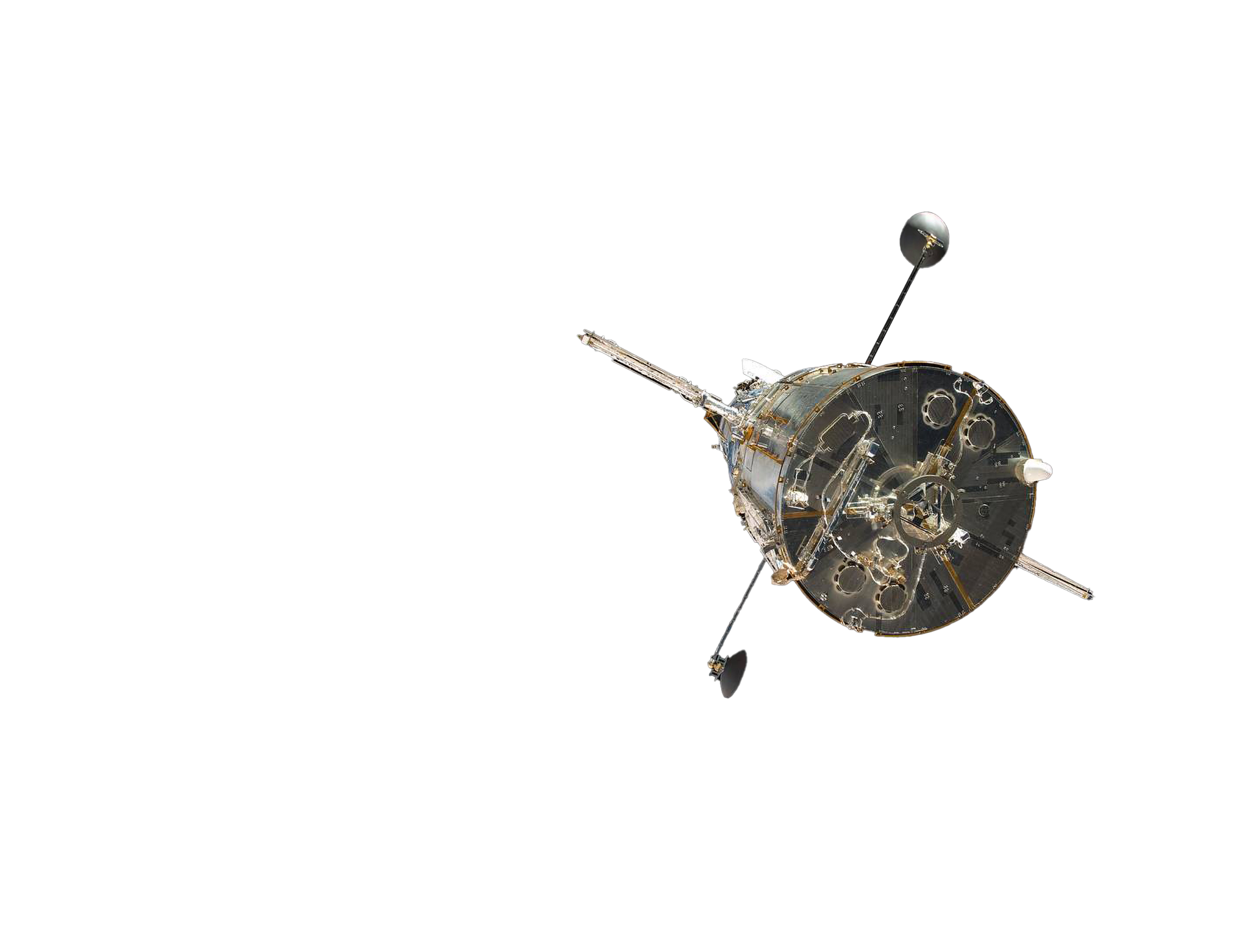
Hubble Space Telescope
The primary mirror blank was made from Corning® ULE® Ultra-Low Expansion Glass. This telescope has allowed scientists to see more than thirteen billion light-years away. Additionally, Corning HPFS was used as a corrective lens to improve the optical performance of the Hubble Space Telescope, allowing the telescope to make clearer observations than ever before.
Image Credit: NASA

Kepler Telescope
The primary mirror blank for the Kepler Telescope was made of Corning® ULE® Ultra-Low Expansion Glass. The telescope also had optical lenses made of HPFS 7980. The Kepler Mission was dedicated to discovering Earth-like planets orbiting stars outside of our solar system. The Kepler Telescope was in operation until 2018 and discovered more than 2,600 planets and over 530,000 stars.




Destiny Nadir Window
The WORF (Window Observational Research Facility) on the ISS contains the highest optical-quality window in space called the Destiny Nadir Window, which is made of HPFS 7980. Images captured from this window have allowed scientists to study floods, avalanches, wildfires, glaciers, ocean events, and more.


Curiosity Rover
HPFS 7979 was used in the camera optics on NASA’s Curiosity rover which landed on Mars in August 2012. The goal of this mission was to learn about the environmental conditions of Mars. The Curiosity rover was the largest ever sent to Mars and included 17 cameras.
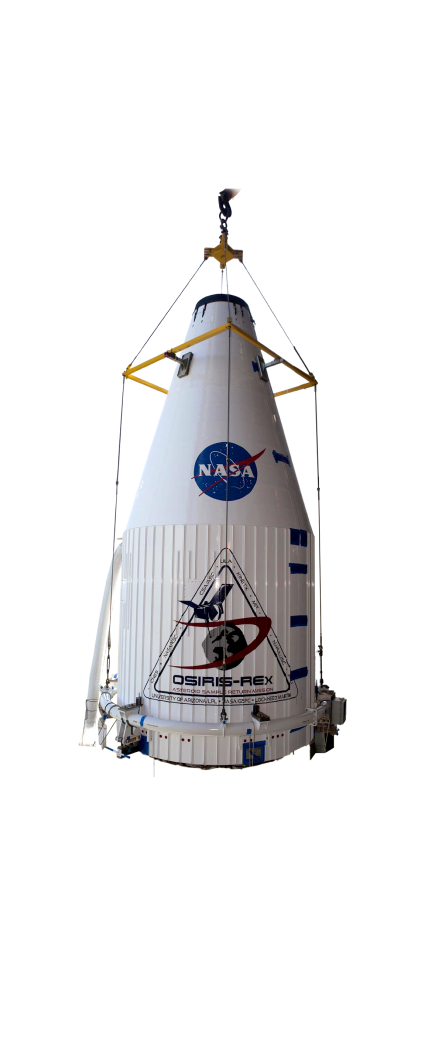
OSIRIS-REx
Corning provided two high-precision mirrors for NASA’s New Frontiers program for asteroid exploration, the OSIRIS-REx mission, to focus on the near-earth asteroid Bennu. OSIRIS-REx launched in 2016 and will return to Earth in 2023. The mirrors help collect and image light reflected by the asteroid.
Image credit: NASA

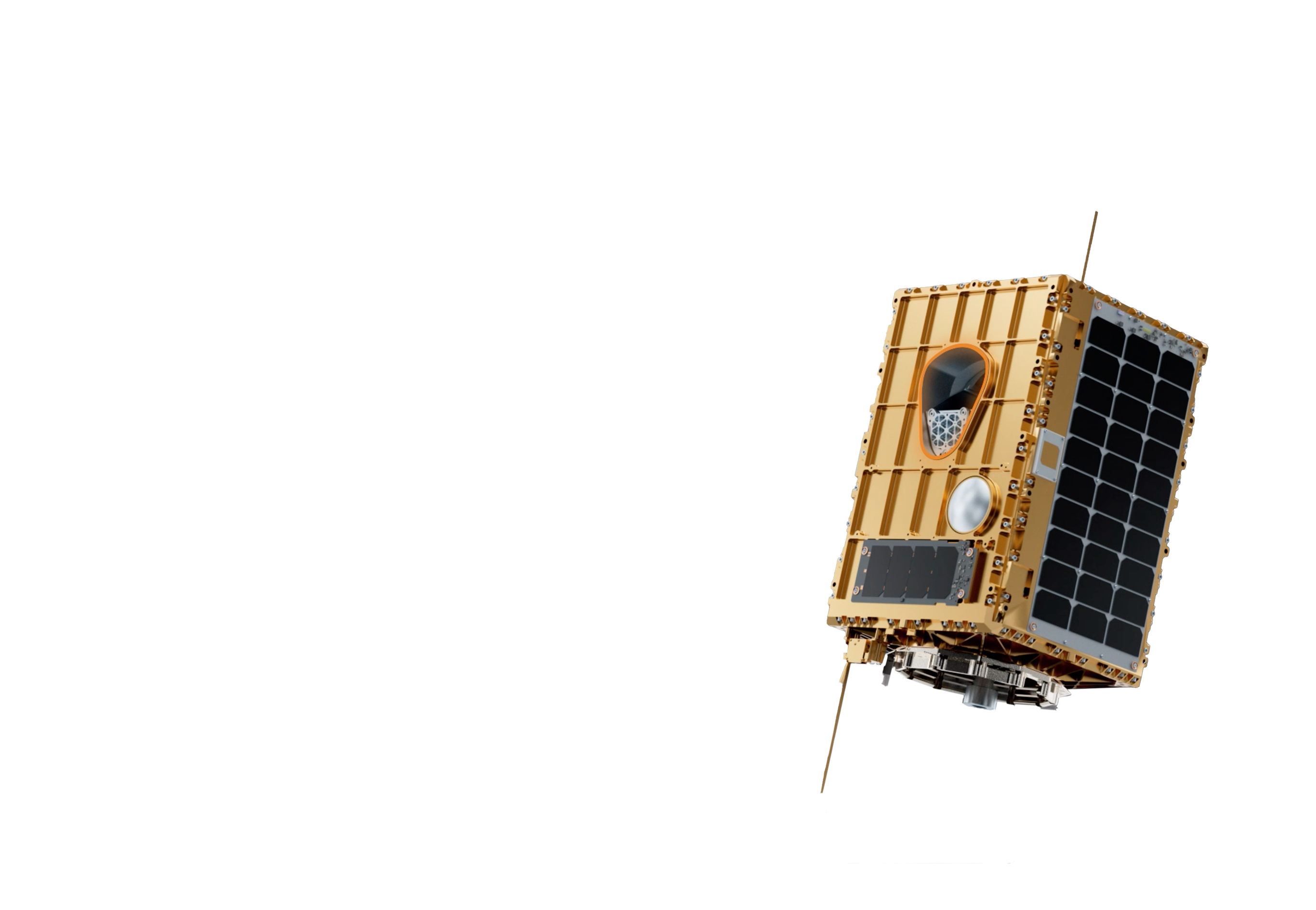
Aurora Satellite
Corning collaborated with Orbital Sidekick on its Aurora Hyperspectral Imaging satellite that will use the highest resolution possible, shortwave infrared light and 30m pixels, to collect data for the energy, mining, and defense sectors and pursue environmental sustainability. The Corning microHSI Model 425 VISxSWIR Hyperspectral Imaging Sensor is on this satellite, and it launched into space aboard the Falcon 9 on June 25th, 2021 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Base in Florida, United States.


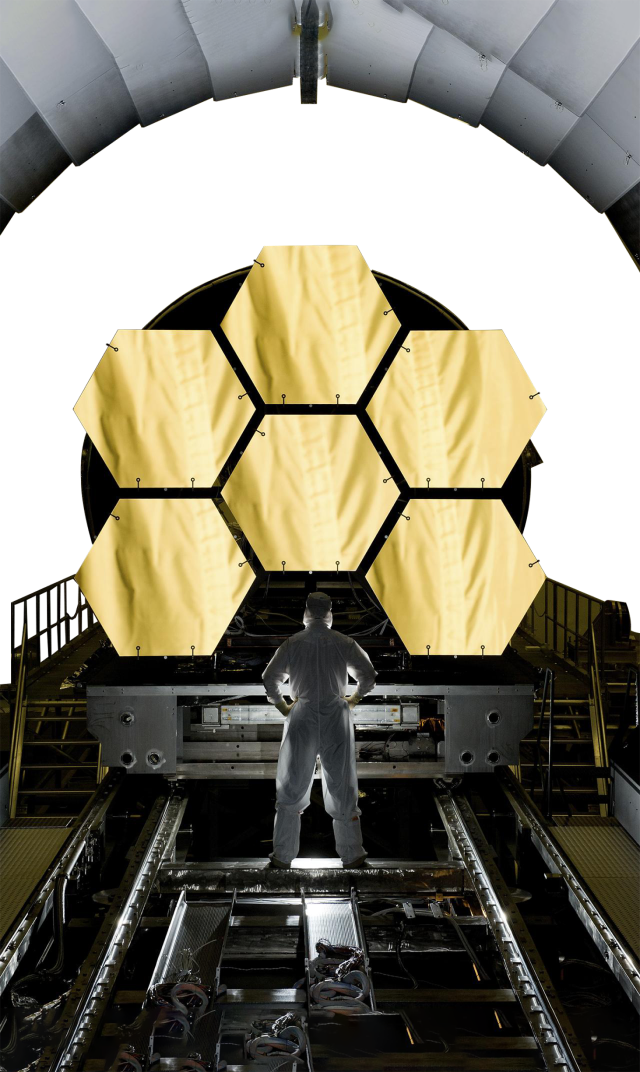
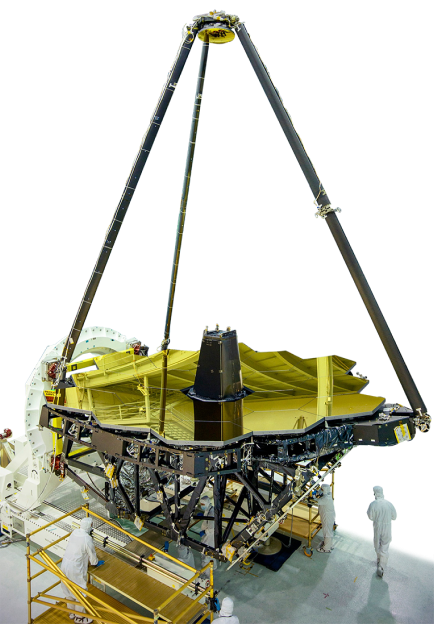
James Webb Space Telescope
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) houses three telescopes with mirrors made by Corning. Corning’s Keene, New Hampshire plant made the Fine Guidance Senor and Tracker Telescopes through COM DEV, as part of the Canadian Space Agencies contribution to the JWST program. This telescope is the largest, most complex space telescope ever built and further extends the work of the Hubble Space Telescope, capturing observations of galaxies, stars, and planets in deep space.
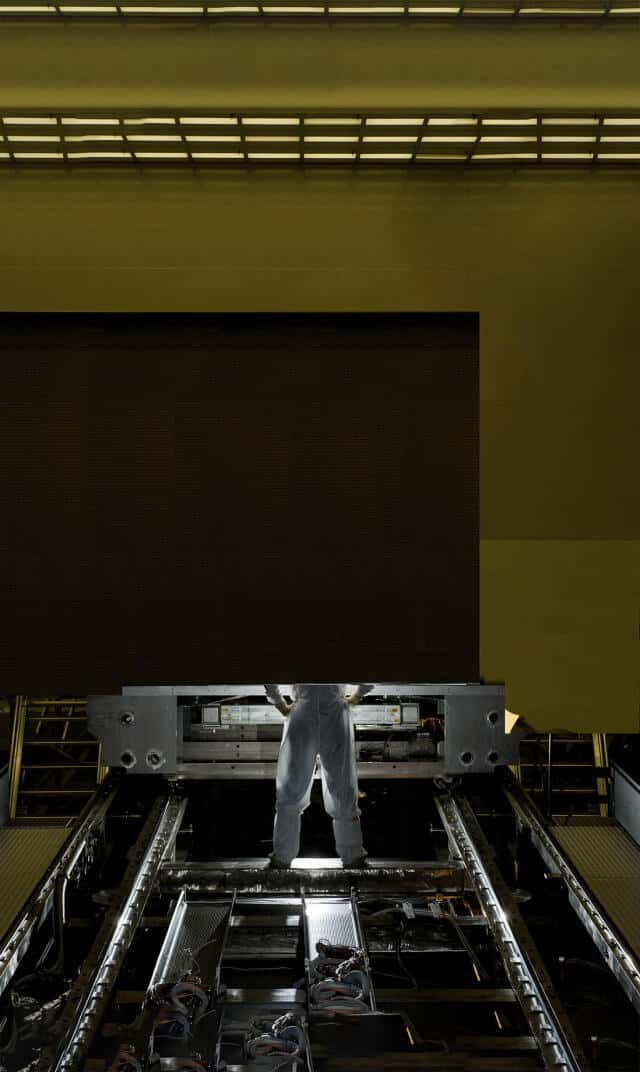
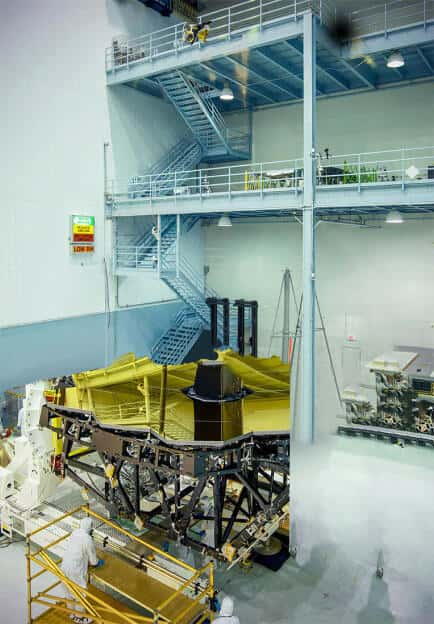



COSMO Large Coronagraph Telescope
Coronal Solar Magnetism Observatory (COSMO) is a facility designed to measure magnetic fields and study plasma in the solar atmosphere. The COSMO will include a 1.5-meter telescope called the Large Coronagraph that will observe radiation emission and space weather conditions over a large field-of-view. The primary lens will be made from HPFS 7980. Upon completion, this will be the largest refracting telescope in the world.